In the fenestration industry, which encompasses the production of windows, doors, and related glazing systems, global supply chains are inherently complex and interdependent. These chains involve sourcing raw materials such as glass, aluminum, PVC, and fiberglass reinforcements from diverse international suppliers, often spanning multiple continents.
Disruptions in these networks can lead to production delays, increased costs, and compromised product quality, ultimately affecting market competitiveness. Effective risk management is essential to ensure operational continuity and long-term sustainability.
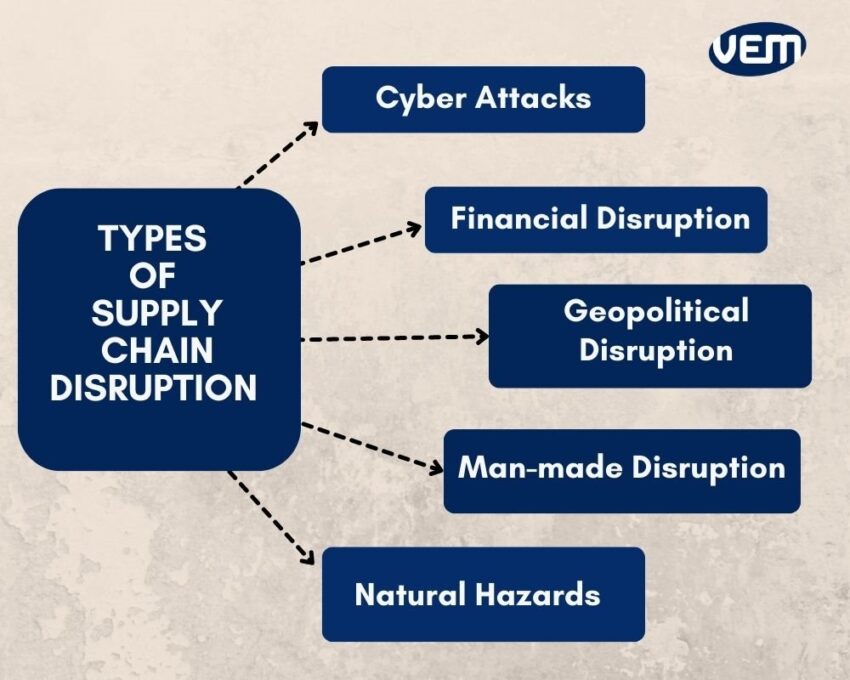
This article examines key risks —geopolitical unrest, natural disasters, and ethical concerns- and outlines practical mitigation strategies tailored to the fenestration sector.
Geopolitical Unrest: Navigating Trade Tensions and Policy Shifts
Geopolitical unrest, encompassing trade disputes, tariffs, sanctions, and regional conflicts, represents a significant threat to global supply chains. In the fenestration industry, where materials like aluminum are frequently imported from regions prone to instability, such disruptions can lead to supply shortages and higher costs. For instance, ongoing tensions may interrupt the flow of critical components, leading to delivery delays and production halts in window and door fabrication.
To mitigate these risks, fenestration manufacturers should diversify their supplier base across multiple geographies, reducing dependency on any single region. Nearshoring or reshoring production elements, such as sourcing fiberglass pultrusions domestically, can further insulate operations from international volatility.
Additionally, regular monitoring of geopolitical developments through specialized risk assessment tools and establishing flexible contracts with alternative suppliers enables proactive adjustments. These approaches not only minimize disruptions but also enhance supply chain agility.
Natural Disasters: Building Resilience Against Environmental Hazards
Natural disasters, including hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and wildfires, pose acute risks by damaging infrastructure, halting manufacturing, and disrupting transportation networks. In the fenestration sector, where raw material extraction and processing often occur in vulnerable areas—such as silica mining for glass production—these events can cause immediate shortages and long-term supply imbalances.
Practical mitigation involves conducting comprehensive risk assessments to identify high-vulnerability points in the supply chain and implementing contingency planning. This may include maintaining strategic inventory buffers for essential components like pultruded fiberglass reinforcements, which provide durability in window frames.
Collaborating with insurers for tailored coverage against disaster-related losses and investing in resilient infrastructure, such as diversified logistics routes, are also effective measures. Furthermore, leveraging advanced forecasting technologies to anticipate environmental threats enables the timely rerouting of shipments, thereby preserving production schedules.
Ethical Concerns: Ensuring Compliance and Reputational Integrity
Ethical concerns in supply chains, such as labor exploitation, environmental degradation, and non-compliance with human rights standards, can lead to regulatory penalties, consumer backlash, and reputational harm. For fenestration products that rely on global sourcing of materials such as timber or metals, unethical practices by upstream suppliers may expose manufacturers to scrutiny under frameworks such as the EU's Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive.
To address these issues, companies should adopt rigorous supplier auditing protocols, including third-party certifications for ethical labor and sustainable sourcing. Implementing traceability systems, such as blockchain for tracking material origins, ensures transparency and accountability throughout the chain.
Engaging in partnerships with ethically aligned suppliers and incorporating ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria into procurement decisions further strengthens defenses against these risks, fostering trust among stakeholders.
Additional Considerations: Economic Instability and Cybersecurity Threats
Beyond the primary risks discussed, economic instability—characterized by inflation, currency fluctuations, and recessions—can amplify cost pressures in the fenestration industry, affecting material affordability and demand forecasting. Mitigation strategies include hedging financial exposures and optimizing inventory management through data analytics.
Cybersecurity threats, such as data breaches or ransomware attacks on suppliers, also warrant attention, potentially compromising sensitive design information or halting digital-dependent operations. Robust cybersecurity protocols, including regular vulnerability assessments and secure data-sharing practices, are critical to safeguard the supply chain.
Conclusion
Managing risks in global supply chains for fenestration products requires a proactive, multifaceted approach that integrates diversification, technology, and ethical oversight. By addressing geopolitical unrest, natural disasters, and moral concerns through targeted strategies, manufacturers can enhance resilience and maintain competitive advantages.
At Tencom, our expertise in pultruded fiberglass solutions supports these efforts by offering reliable, domestically produced reinforcements that reduce exposure to international disruptions. As the industry evolves, ongoing vigilance and adaptation will be key to navigating an increasingly uncertain global landscape.





.jpg)