In the world of construction and manufacturing, there are many materials used to create strong and reliable products. Engineers need to be aware of the materials that can help them develop reliable products that function as intended by users.
Fiberglass and fiber-reinforced polymers (FRP) are two such materials. These terms are often used interchangeably, though there is technically a difference between the two.
Understanding the differences between materials can help engineers choose the best material for their product.
What is Fiberglass?
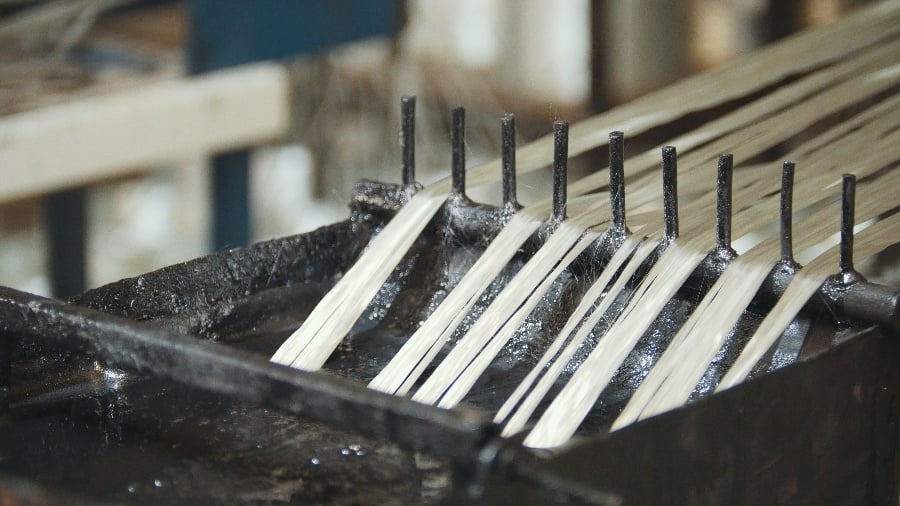
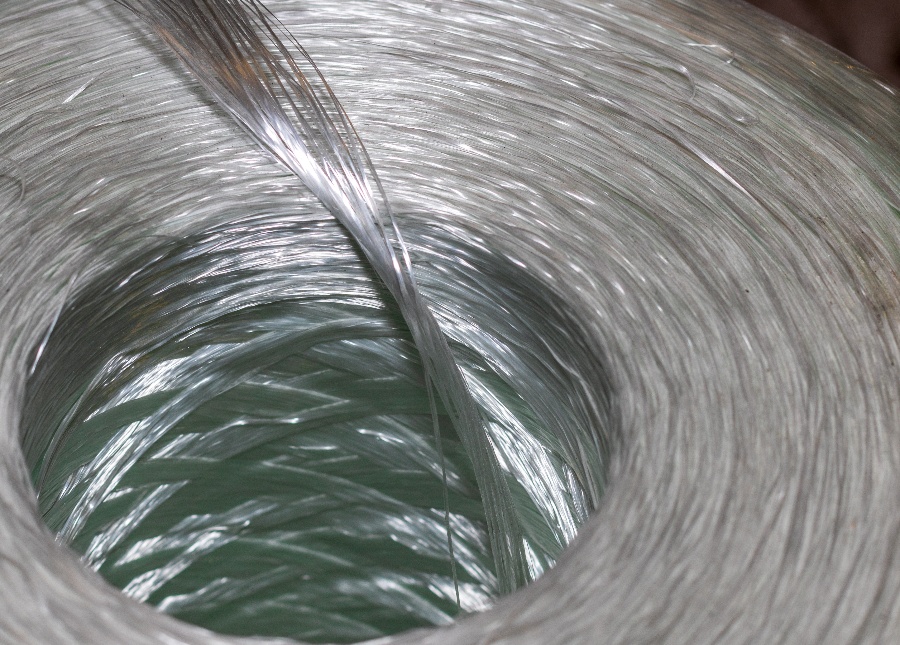
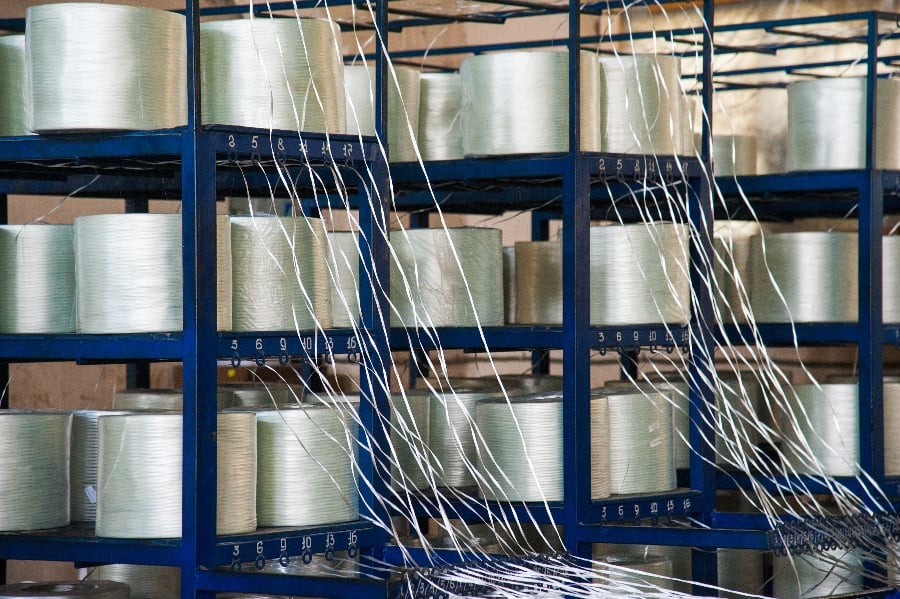
Fiberglass is made by spinning molten glass into glass fibers. Minerals, such as limestone or silica sand, are placed in a furnace until they reach their melting point. The melted material is then extruded through tiny orifices, known as brushings, to create filaments. The filaments are then coated in a chemical finish and bundled together into rovings. The overall weight of the fiberglass is determined by the number of filaments in the roving and the thickness of the individual fibers.
These fibers can be used on their own or in a composite, which is a combination of materials that creates a new substrate. The matrix of a composite can be metal, plastic, or even ceramic, with fiberglass acting as the reinforcement material that makes the composite stronger than its parts on their own.
It is used in a variety of applications, including thermal insulation and reinforcing composite materials. When used as insulation, fiberglass is typically available as blankets or rolls. It is installed between studs in walls, on attic floors, and around pipes and ductwork. Fiberglass insulation is known for its high R-value, which measures its ability to resist heat flow.
Fiberglass is an ideal reinforcement for printed circuit boards in computers and other electronics, serving as an electrical insulator and a resistive material. The rising demand for PCBs in consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications products is driving demand for fiberglass fabrics.
When used as a reinforcing agent, fiberglass can greatly improve the strength and durability of composite materials. The aerospace and automotive industries often use fiberglass composites in the construction of aircraft and vehicles. Overall, fiberglass is a versatile material with a wide range of potential applications.
What is FRP?
Fiber-reinforced polymers are a type of composite material. As the name suggests, they are made up of two primary constituents: fibers and a polymer matrix. In an FRP, the fiber is embedded in the polymer matrix. This structural arrangement confers entirely different chemical and physical properties on the materials than those of the individual constituents.
FRPs offer a number of advantages over traditional materials, but one of the most significant is the inherent advantage of their manufacturing process. Pultrusion is an automated composite manufacturing process that pulls fiber rovings through a resin bath, impregnating and reinforcing them to create a strong, lightweight material. The entire process can be completed quickly and on a large or small scale without compromising quality. As a result, FRPs are an excellent choice for a wide range of applications.
FRP composites are lighter than steel and concrete, yet they have a high strength-to-weight ratio. They also offer superior corrosion resistance and durability. As a result, FRP composites are an increasingly popular choice for a wide range of applications.
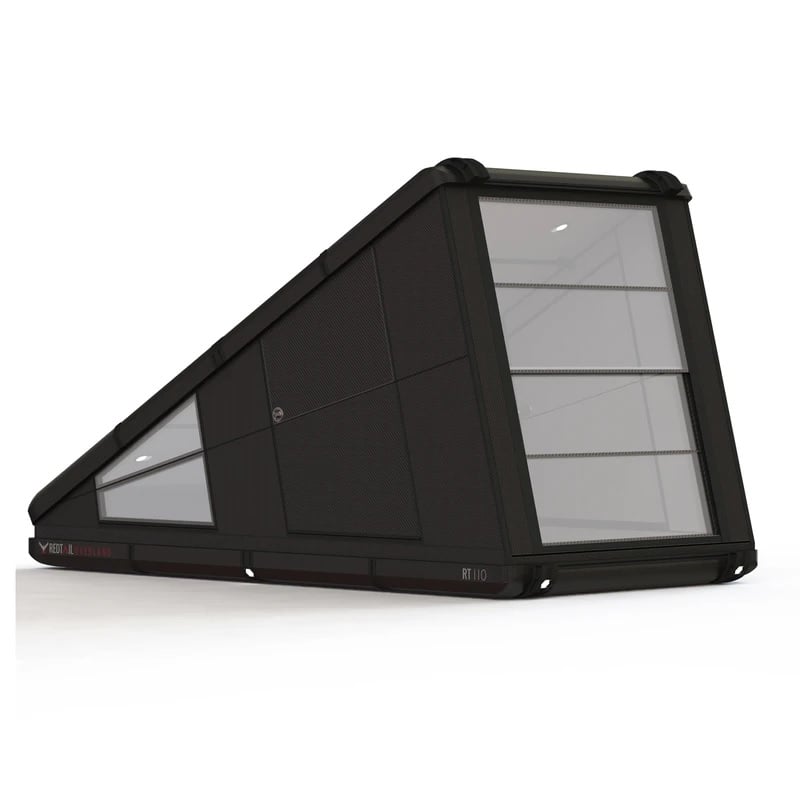
FRPs are becoming increasingly popular in a variety of industries due to their exceptional performance properties. For example, FRP doors and windows are resistant to a wide range of corrosive substances and extreme temperature fluctuations. In addition, FRPs are lightweight, have excellent electrical and thermal insulation, and exhibit high stiffness.
FRP Advantages
Lasting Sustainability
As sustainability becomes increasingly important to consumers and manufacturers alike, companies are innovating to meet these needs. One way they are meeting these requirements is through durability. FRPs are durable, meaning they’re not replaced as frequently as traditional materials like concrete and steel.
Products made with FRP often weigh less than those made with traditional materials. The lower weight of composite products results in lower energy consumption, which in turn reduces CO2 emissions. This lower weight is crucial in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Reduced Costs
In addition to their environmental advantages, FRPs also offer economic benefits. Because they last longer, manufacturers don’t have to replace them as often, saving money in the long run. Companies may also spend less capital on maintenance, and because they’re lighter, they can often be shipped at a lower cost than traditional materials.
Additionally, pultruded products are substantially cheaper to manufacture than traditional materials. This reduced cost enables increased budgets and improved resource allocation without compromising quality or performance.
Unique Designs
FRPs can be formed into nearly any shape imaginable, enabling structures and designs that would be impossible or impractical with traditional materials. Engineers can use FRPs to develop unique designs with the colors they desire. During the production process, FRPs can also be custom colored or painted after production. For example, FRPs can be shaped into complex curves or even woven into fabric-like structures.
Overall, FRPs offer several advantages over traditional materials such as fiberglass. They are stronger, more durable, and more resistant to damage. As a result, they are often the preferred choice for products that require high-performance standards.