Roll-up doors, also known as roller doors or overhead doors, are essential components in many industrial, commercial, and residential settings. These doors provide convenient access while also serving as protective barriers when closed. As seemingly simple mechanisms, the engineering behind roll-up doors is critical for optimal safety, security, durability, and functionality.
Engineers must consider a variety of factors when designing roll-up doors, including anticipated wind loads, integration of locking mechanisms and access control, insulation requirements, corrosion resistance, constraints on installation space, and flexibility for frequent use over an extended lifetime. Material selection also plays a vital role in meeting strength, weight, thermal conductivity, and cost requirements.
This article provides an overview of key design considerations for engineers looking to specify, test, or install roll-up doors.
Roll-Up Door Design Considerations
Accounting for expected loading conditions and environmental exposures is paramount to roll-up door selection and installation. Careful analysis during the design process helps ensure safety, security, and durability over the door's service life.
Load and Stress Analysis
Engineers must calculate anticipated wind loads and specify adequate structural reinforcements. Determining wind pressure to select doors with sufficient wind load ratings prevents failures or damage. Analysis of the supporting structure helps identify reinforcement needs and appropriate mounting hardware.
- Wind Load Calculations: Calculate wind pressures based on door size, location, and relevant building codes. Specify doors rated for expected wind zones.
- Structural Support Requirements: Analyze header beams, side columns, and mounting anchors to withstand wind and impact loads. Reinforce support to meet code requirements.
Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions, both inside and outside the building, can impact door performance and longevity. Carefully consider factors such as:
- Corrosion Resistance: Select door materials and finishes to withstand humidity, ocean air, caustic cleaners, or other exposures.
- Temperature Extremes: Specify door components rated for minimum and maximum service temperatures. High R-value insulation helps regulate interior temps.
Proper door selection combines analysis of strength requirements, expected exposures, security needs, and installation constraints. Doors that meet structural load capacity often fail prematurely without accounting for environmental factors in the design process. Careful consideration of both loading conditions and the service environment ensures optimal safety and performance.
Roll-Up Door Material Properties
The performance and longevity of roll-up doors depend heavily on the inherent properties of door materials. Carefully evaluating common material choices helps strike the right balance of strength, weight, insulation, and cost.
Proper material selection provides the required combination of:
- Tensile Strength and Durability: Materials must withstand years of frequent opening/closing without fatigue failure. High tensile and yield strength is needed to resist wind loads and impacts.
- Corrosion Resistance: Metals and finishes must resist corrosion from exterior and interior exposures over decades of service.
- Thermal Conductivity: Insulated doors with low U-factors and high R-values reduce heat transfer for energy efficiency.
- Flexibility and Impact Resistance: Doors experience millions of roll-up cycles requiring flexible, resilient materials that resist cracking or deforming during use and abuse.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratios: Lighter doors require less structural support during installation and reduce stresses on lifting mechanisms. But adequate thickness and reinforcement is required to provide necessary strength and rigidity.
Considering door material properties during the design process ensures selected products withstand expected load conditions while meeting project goals for security, thermal insulation, weight restrictions, and budget constraints over decades of reliable operation.
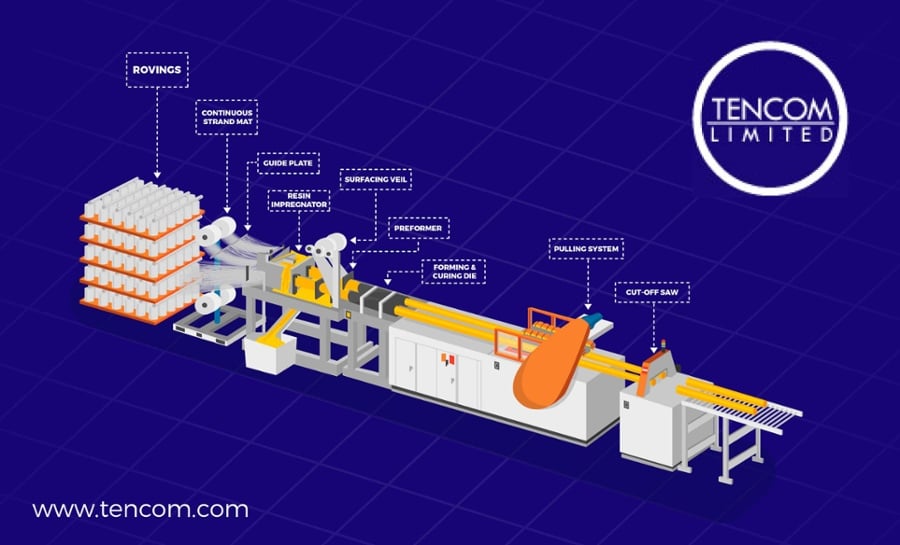
The Benefits of Fiberglass Roll-Up Doors
Fiberglass offers an advantageous combination of strength, durability, and lightweight properties that make it an ideal material for many roll-up door applications. Compared to metals, fiberglass doors provide greater insulation value for reduced heat transfer through doors. The material also resists corrosion from weather exposures or caustic cleaners.
Strength & Impact Resistance
The woven roving construction of fiberglass doors imparts high tensile and flexural strength to withstand wind loading and impacts. The doors bounce back after collisions thanks to their resilient properties. Industrial-grade fiberglass doors rate for hundreds of thousands of life cycles.
Lightweight
Pound-for-pound fiberglass possesses four times the stiffness of steel while weighing much less. The high strength-to-weight ratio allows lighter doors that put less demand on lifting mechanisms. This permits larger door sizes before requiring electric openers.
Durability
Properly formulated fiberglass resists UV degradation, maintaining visual appeal over decades of service. The material withstands a wide temperature range from -40°F to 120°F while retaining flexibility. Fiberglass won't fatigue or crack over years of roll-up cycles.
Low Thermal Conductivity
In addition to composite and foam-insulated cores, the fiberglass skins provide an insulating barrier. Coupled polyurethane insulation helps minimize heat transfer through roll-up doors. This reduces energy costs for conditioned spaces.
Specifying high-quality fiberglass roll-up doors takes advantage of the material's impressive strength, resilience, and insulation properties. Fiberglass represents a lighter, more durable, and corrosion-resistant alternative to traditional steel doors for many standard or custom applications.